Leverage Trading
What is Leverage?
Leverage is one of the most important features of forex and CFD trading. It is a powerful tool that allows traders to gain greater exposure by opening positions that are significantly larger than the amount required to open the trade. To open positions, a trader is only required to have the margin requirement present in their trading account.
This is known as margin trading and is a concept used when trading financial markets using advanced trading platforms such as MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5 and Iress. It is important to understand how leverage works before you start trading. This will allow you to maximise returns and limit potential losses by utilising risk management tools.
Leverage Key Terms?
To get a clear understanding of leverage there are a number of key terms that you need to be aware of. They are:
Initial Margin: The amount of money required to open a trading position.
Margin: The total amount required to open and maintain a trading position. This includes the initial margin, any brokerage charges such as swap rates required to maintain a position overnight, and any potential margin call.


Leverage Ratio: Put simply, it is the amount of exposure you are able to gain with respect to the capital invested. It can range from 2:1 (twice the initial deposit) with high leverage amounts up to 30:1 (30 times initial deposit).
Using the above, leverage refers to the use of borrowed funds to magnify the size of a trading position. Traders do not need the total value of the trade available in their account balance. Instead, they are only required to deposit the initial margin to open a position but will gain exposure to a significantly larger amount depending on the leverage offered.
For instance, you are able to trade with a leverage ratio of 10:1. This means that you will be able to open a position that is ten times the size of the initial deposit. With only $1,000 present in your trading account, you would be able to open a position with a total value of $10,000.
How does
Leverage Work?
The use of leverage is common in the forex market and its benefit can be shown through a simple comparison to trading stocks. With conventional stock market trading you are required to pay for the total value of the shares that you wish to purchase. Let's assume you wish to purchase 1,000 Woolworths shares at a price of $50 per share. You would need $50,000 to execute the trade.
In comparison, if you were to purchase a share CFD which offered a leverage ratio of 20:1, you would only need to 5% of the total value of the position. In the above scenario, you could gain exposure to $50,000 worth of Woolworths shares with only $2,500. Similarly, a $50,000 investment would allow you to gain an exposure of $1,000,000 (20 times your initial investment).
Different Types of Leveraged Products
FP Markets offers leveraged trading on 10,000+ financial instruments across the largest global markets. This allows traders to capitalise on market volatility by taking advantage of even the smallest price movements. The most popular leveraged products are forex and Contracts For Difference (CFDs).
Forex
Leverage is one of the main contributing factors to the meteoric rise of forex trading. With trading turnover in the trillions per day, the forex market is the largest financial market in the world. Trading forex involves buying one currency and selling the other simultaneously.
Contracts for
Difference (CFDs)
CFDs are a contract where you exchange the price difference of an underlying asset without actually taking ownership of it. One of the main attractions of CFD trading is that they are a leveraged product.
Other
In the financial services industry there are a number of other leveraged products including futures, options, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Which Markets Can You Use Leverage on?
At FP Markets, our range of leveraged products includes forex and CFDs in shares, commodities, metals, indices, and cryptocurrencies. Here is a detailed look at the markets that you can use leverage on.
Forex
Currency pairs
in forex are separated
into three
categories:

Majors
Include the US dollar as a base or quote currency, are the most traded pairs, and have the tightest spreads. Examples are EUR/USD and AUD/USD

Minors
Are made up of prominent currencies but do not include the US dollar. Examples are GBP/CAD and EUR/AUD.

Exotics
Can include a major currency with an emerging market currency. Higher volatility and less liquidity generally means wider spreads for exotics. Examples are AUD/MXN and JPY/NOK.
CFDs
FP Markets offers leveraged CFD trading in a number of products including:
10,000+ Australian and international share CFDs across four continents. Trade the biggest companies in the world including Apple, Facebook, Alphabet, Tesla, and Walmart.
Enjoy leveraged trading on major commodities such as West Texas Intermediate Crude Oil (WTI), Brent Crude Oil, and natural gas. With negative correlation to traditional asset classes, commodities are often used as part of a risk management trading strategy.

With FP Markets, you can trade CFD indices futures from across the world at margins starting at just 1%. Trade the largest global exchanges including the NYSE, NASDAQ, LSE, and ASX.

Buy and sell cryptocurrency without the need for a digital wallet. Trade the most popular cryptocurrencies including Bitcoin, Ethereum, XRP (Ripple), Bitcoin Cash, and Litecoin using cryptocurrency CFDs.
Pros and Cons
of Using Leverage
There are a number of advantages that leveraged trading provides, but it is essential to understand the risks associated. This will help you maximise your profits while limiting your risk exposure.

Advantages
Increased profit potential: Through access to additional funds than are available in your account, you can increase your potential profits by trading with leverage. With the amount required to open a position limited to margin, your profits from trading can be amplified.
No interest: Despite gaining access to more funds, no interest is payable. Any normal associated with the purchase of any other asset would have an interest payable associated to it. When trading with leverage, FP Markets provides the additional amount required to open the trade without charging any interest.
Low barriers of entry: With FP Markets, you can open a trading account with as little as $100. Depending on the instrument traded, you could open positions with a total value in the thousands using leverage.
Hedging: Leverage can be utilised effectively when hedging as part of a risk management strategy. It allows investors to hedge against risk without having to outlay a substantial amount of capital.
Trading Opportunities: A range of leveraged products such as forex can be traded 24 hours a day, 5 days per week. Combined with the ability to trade in both directions (open long and short positions), this creates more trading opportunities.
Drawbacks
With the ability to open significantly larger positions, traders should also be aware of the potential drawbacks associated with leveraged trading. These include and are not limited to:
Magnified losses: While the use of leverage can increase your profit potential, it may also magnify your losses. This is why it is important to develop a trading plan which considers your risk appetite and provides strategies to manage market volatility. Inexperienced traders can practice using a Demo Account which allows you to learn and test strategies using virtual currency.
Margin Call: There is always the possibility that you could lose more than the amount in your trading account. If your losses exceed your account balance, you may be issued with a margin call. The use of risk management strategies such as the use of stop-loss orders can prevent this from occurring.
Trading Costs: Depending on the size and type of your position (long or short), there may be fees associated with maintaining these positions overnight. Swap rates and other charges should be accounted for prior to executing any trades.
This further emphasises the need to employ risk management techniques and strategies while trading.
Which Markets Can You
Use Leverage on?
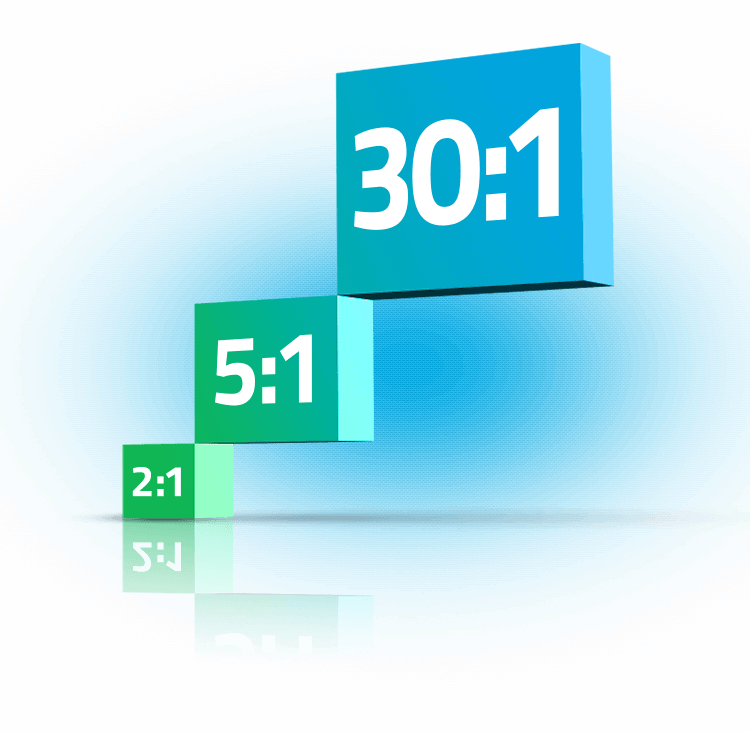
Leverage ratio relates to the amount of exposure you are able to gain with respect to your initial investment. The amount of leverage offered will vary depending on a number of factors including the financial instrument being traded, position size, and account type.
The typical leverage ratio offered on retail investor accounts ranges from 2:1, 5:1, and up to 30:1. Those who wish to trade on higher leverage should explore our FP Markets Pro Account. Eligible clients are eligible for a maximum leverage amount of up to 30:1 on several products including major currency pairs, gold, and oil.
What does
the Leverage
Ratio Represent?
The leverage ratio represents the proportion of debt with respect to the amount of equity/capital. The capital is generally represented by the number 1 with the other the proportion of debt that a trader can access. A leverage ratio of 20:1 means that a trader can gain exposure equivalent to twenty times their capital. Similarly, this can be explained in the opposite way. That is, the margin requirement is 1/20th or 5% of the total value of the trade.
Types
of
Leverage Ratio
In the financial services industry, the most common types of leverage ratios are:
Debt to Assets Ratio = Total Debt / Total Assets
Debt to Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Total Equity
Debt to Capital Ratio = Today Debt / (Total Debt + Total Equity)
Debt to EBITDA Ratio = Total Debt / Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortisation
Asset-to-Equity Ratio = Total Assets / Total Equity
Leverage Trading FAQ
To help display how leverage is calculated, let's look at two traders, Trader A and Trader B.
Trader A: ($1,000/5:1)
If Trader A has an account leverage of 5:1 and they wish to use $1,000 on one trade as margin, they will have exposure of $5,000 in base currency ($1,000).
5 x $1000 = $5,000 (trade value).
Trader B: ($1,000/30:1)
If Trader B has an account leverage of 30:1 and they wish to use $1,000 on one trade as margin, they will have exposure of $30,000 in base currency ($1,000).
30 x $1000 = $30,000 (trade value).
Comparison
Trader B could open a position with the same value as Trader A using only a fraction of the $1,000 in their trading account. As the margin requirement of Trader B is only 3.33% (30:1), they would be able to open a position with a value of $10,000 with just $333.
$10,000 x 0.033 = $333
Leverage is regularly used in forex and CFD trading. The leverage level will vary depending on a number of factors including the financial instrument being traded, account type, trader experience, position size, and regulation. Higher leverage levels are generally available for products with high levels of liquidity such as major forex pairs and indices. With respect to trading share CFDs, view FP Markets margin requirements.
There are several factors that need to be considered when finding an optimal leverage ratio. Traders should be aware of their risk appetite and stick to a trading plan. Experienced traders are more comfortable trading with a higher leverage ratio while inexperienced traders should consider starting with a lower leverage ratio. In addition to this, the financial instrument being traded should also be considered. Some markets such as cryptocurrency are recognised as being more volatile than heavily traded products including major currency pairs.
With respect to online trading, a leverage ratio of 30:1 means that for every $1, you can trade up to $30 of a financial instrument. In some countries, the maximum leverage ratio on retail investor accounts is 30:1. The leverage ratio will vary across asset classes and financial instruments. Traders should always be aware of the leverage ratio that they are trading with and adjust their strategy accordingly.
What is a 500:1 leverage on FP Markets Pro Account?
What is a 500:1
leverage on
FP Markets Pro Account?
At FP Markets, we welcome experienced and professional traders. As a result, we have specifically designed the FP Markets Pro Account which allows eligible traders to maintain a maximum leverage ratio of 500:1. This is available on a number of instruments including major forex pairs, minor forex pairs, and gold. Pro Account holders have access to dedicated account managers and referral incentives. For an uninterrupted trading experience, apply to upgrade today!