Experience Trading
on the Go
on the Go
Where Should
You
Start?
Perhaps the most defining thing about 2020 has been the coronavirus outbreak. The pandemic affected everything, from something as far-ranging as the global economy, to the way we work and communicate as individuals.
However, not everything can be blamed on the pandemic. The global economy and the financial markets were also impacted by the trade tensions between the US and China and diplomatic tensions between the UK and Europe over Brexit. All these events wreaked havoc on global stock markets and saw stock prices plummet. They also led to significant and continuous changes in the demand for currencies. This is due to several factors, like reductions in interest rates, governmental stimulus packages, restrictions on businesses, changing trade balances and unemployment. Forex trading was also impacted by trading in other markets. For instance, when the stocks of a country rally, it boosts the local currency. Similarly, if the commodity market experiences a surge, commodity currencies like the Canadian dollar and the Australian dollar tend to rise.
What was the Impact
of Covid-19
on Forex
Trading?
The coronavirus outbreak began in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019. What was initially thought to be a short-term problem quickly spiralled into a global pandemic. It’s not surprising that that first currency to be impacted by covid-19 was the Chinese yuan. Almost immediately, the Australian dollar also came under pressure, as China is Australia biggest trading partner.
Soon the virus spread to Southeast Asia where currencies like South Korea’s won (KRW), Malaysia’s ringgit (MYR) and Thailand’s Baht (THB) started to feel the pressure. In February, covid-19 had started spreading to Spain, Germany, Italy, France, and the UK. The euro and pound tumbled, but the impact was not limited to these currencies. With travel restrictions, businesses being forced to close offices and factories, and supply chain disruptions, investors started fearing for the global economy. Such sentiments led investors to prefer safe-haven assets, like the Swiss franc, US dollar and Japanese yen, all of which gained during the crisis in Europe.
In March, the virus outbreak was termed a pandemic. The next country to be hit was the US. Infections began climbing by April and, by July, the US had become the hotspot. Although the US dollar (USD) is considered as the “currency of last resort”, it plummeted in the face of rising infections leading to record unemployment and economic contraction. The NASDAQ plunged with record amounts being wiped off the market price as stock traders on Wall Street ran for cover.
As the events unfolded, the global financial markets become increasingly volatile. Investors and traders saw numerous attractive opportunities and trading volumes grew significantly. This was especially so for the forex market. The reasons why the forex market witnessed a spike in trader accounts and volumes are:
Stranded at home, people had more time to learn trading.
Threatened by declining business and fewer job opportunities, people wanted to supplement their income with other sources.
New traders tend to start their trading journey with the forex market.
Why Do Beginners
Prefer the
Forex
Market?
Consider this as a beginner's guide to forex trading.
Most new traders begin their trading experience with the forex market. This is because they find the currency market dynamics easier to understand. Moreover, forex is the world’s largest and most liquid market. It recorded an average daily volume of $6.6 trillion in 2020.
The forex market is also highly accessible. It is open 24/5 because it covers four major market sessions based on timings - the Sydney session, the Tokyo session, the London session, and the New York session. Being readily accessible, the currency market allows a trader significant flexibility to determine when to trade and what strategy to follow. New traders should be aware that deeper liquidity in a particular pair exists at the time when its particular market is in sessions.
For instance, the best time to trade a currency pair involving the Australian dollar (AUD) is during the Sydney session. Similarly, the British Pound (GBP) and US Dollar have the highest levels of trade during their respective London and New York sessions. This is even more important for those looking to conduct short term trading as doing so will minimise trading costs. Holding positions for less than a day is a trading strategy commonly referred to as swing trading.
The low commissions involved in trading forex is also an attractive proposition for newcomers. Forex trading has lower costs and fees than other markets which makes it a desirable option for day trading. In fact, certain brokers offer zero commission, which means they don’t charge anything and make their money from the difference between the bid and ask rate (known as the spread).
What is
Market
Analysis?
A major part of trading is deciding the prices at which to open and close positions. This requires a trader to analyse the market and the various factors impacting it. Novice traders often feel overwhelmed with the vast number of factors that impact the forex market. Here is a simple way to understand the factors affecting your analysis.
Broadly speaking, there are three types of market analysis. This is not merely for forex trading, but for trading any financial instrument, including stocks, indices, and commodities. The three types of market analysis are:
Fundamental Analysis – based on intrinsic market values
Technical Analysis – based on the past performance of the price of a financial instrument
Sentiment Analysis – overall mood and attitude of traders in the market
These are all ways to understand the market dynamics, set up trading strategies and identify possible open and close positions. There is no magic formula to determine which way the market will actually move with most day traders employing simple methodology in their strategies.
What is
Fundamental
Analysis?
Fundamental analysis is based on factors that affect the economy. In doing so, it takes into account current factors as well as predictions of future factors. They include both economic and noneconomic factors:
Economic Factors:
GDP
Inflation rate
Interest rate
Balance of Trade
Balance of Payments
Government Debt
Traders can stay in touch with the important economic indicators by accessing a comprehensive economic calendar.
The most important economic indicator for forex traders is the interest rate. This is because a higher interest rate attracts more investors to the country, which increases the demand for the local currency. This increases the value of the country’s currency. On the other hand, if interest rates are too high, it leads to the problem of high inflation, which discourages investors as the prices of raw materials are higher. Moreover, inflation erodes the value of that country’s currency.
Another significant market moving economic indicator is the US NFP (nonfarm payroll) report, which gives an overview of the employment market in the world’s largest economy. Investors, traders, analysts, and fund managers look out for this report, which is released on the first Friday of every month at 8:30am EST. A higher-than-expected payroll figure indicates more job additions in the US. This suggests a healthier economy, as people have more money to spend on goods and services, leading to economic growth. On the other hand, a lower-than-expected payroll figure is detrimental for the American economy.
Non-economic Factors:
Political environment
Natural disasters
Maturity of the domestic capital market
Forex traders can remain abreast of important non-economic events by staying in touch with the news. The most important factor among these is the political landscape of a country. Any political unrest within a country or deterioration in diplomatic relations with other countries discourages investors. This reduces demand for the local currency, leading to a decline in the currency’s value over time.
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis is based on the past price movements of a particular financial instrument. The idea is that past trends influence future price movements.
Technical analysis is based on 3 important tenants:
1.
The market discounts everything: Traders and investors respond to every event in the economy or socio-political environment. So, in time, all factors that influence a financial instrument are reflected in its price. This includes fundamental factors too.
2.
Trend is your friend: Prices of financial instruments move in trends and have the tendency to remain within the trend. So, once a trend has been set, the price of the security will move in the same direction as the trend.
3.
History repeats itself: Most price movements of securities will form patterns and these patterns will be repeated. This is due to market psychology, as traders and investors are likely to respond broadly in the same way to similar price movements.
Traders use technical charts, technical indicators and various analytical tools to determine trends in price movement to make predictions. Using these charts, traders are able to recognise repeated chart patterns, which are then used to predict the future movement of the market.
These tools help a trader determine whether the price of the financial instrument is likely to rise or fall in the future. Depending on this, traders can determine whether they wish to buy or sell the financial instrument.


What are the Types of Charts?
A chart is essentially a visual representation of the price movement of a security over a defined period of time. In the chart, the vertical axis (y-axis) represents the price of the financial instrument, while the horizontal axis (x-axis) represents the timeframe. As you move from the left to right, the chart shows price movements in the most recent period.
Before we delve into the types of charts, it’s important to understand the four most important prices of a security during a trading day. These are:
Opening price: Price of the security when the market opens for trading
Closing price: Price of the financial instrument when the market ends the trading day
High: The highest price achieved by the security during a trading day
Low: The lowest price for the financial instrument during a trading day
Some traders ignore the day’s high and low price-points and focus only on the opening or closing price. This enables them to ignore intraday price swings. Between the opening and closing price, traders often give more importance to the latter.
Bar Charts
A bar chart provides more comprehensive information than a line chart, as it shows the opening and closing prices as well as the high and low of a particular security during a trading day. This is a very quick visual representation of how the security performed throughout a trading day and what the volatility level was.
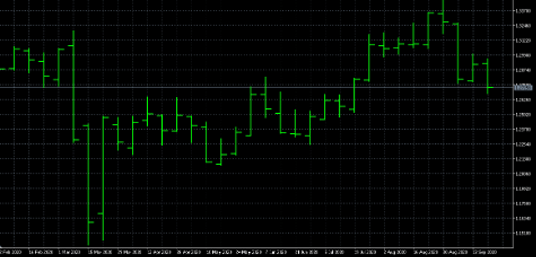
The top and bottom of the vertical bar represent the high and low price of the security, while a horizontal dash on the left side of the vertical bar represents the opening price and one on the right illustrates the closing price. This is why a bar chart is also known as the OHLC (open, high, low, close) chart. A bar chart indicates the level of volatility of the security.
The three main types of charts are:
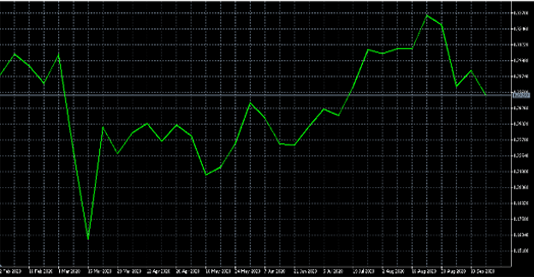
Line Charts
A line chart is typically used to get a bird’s eye view of the market or see the bigger picture of price movements. The line chart is formed by connecting the financial instrument’s closing prices over a period of time.
Candlestick Charts
This has made it to the list of the most used charts because it is a very simple way to get all the important information of trading on a particular day and view the price movements over time in an easy-to-read format.
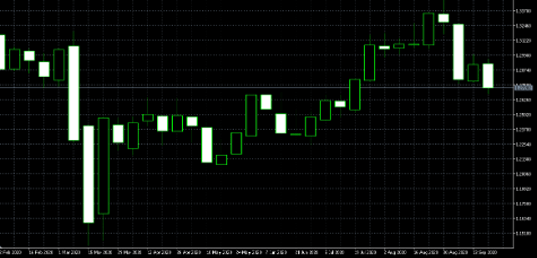
How to Do Market Analysis with Candlestick Charts?
Candlestick charts are similar to bar (OHLC) charts but are able to convey a lot more information in a very easy-to-read format. The horizontal lines indicate the open and close of a trading day. These are connected by vertical lines to form a box, which is known as the body of the candlestick. A vertical line is drawn above the box to represent the trading day’s high and a vertical line below the box shows the low of the trading day. These vertical lines above and below the box are known as wicks or shadows.
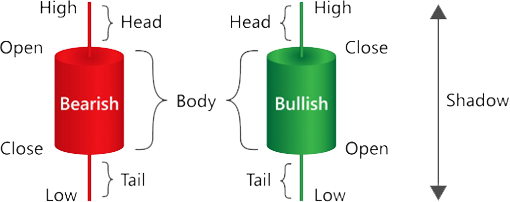

The length of the vertical line above the candlestick is known as the head and represents the difference between the highest price during the trading day and either the open or close price, depending on which is higher. The length of the vertical line below the candlestick, known as the tail, is the difference between the lowest price of the trading day and either the open or close price, depending on which is lower. The length of the main body of the candlestick is the difference between the open and close price.
The body of a candlestick chart can be coloured red or green (or hollow and filled) to represent a decline or rally in prices. If the closing price of a security is higher than the open, the body is coloured green (or left hollow), while if the close is lower than the open, the body is closed red (or filled). Therefore, just by looking at the colours, traders can easily know whether a security has been having mostly up days or down ones.
If the close price is higher than the open price, this is referred to as a bullish candle, while if the close price is below the open price, it is called a bearish candle.
Price charts and charting tools can be accessed within most of the online trading platforms offered by forex brokers. Traders can change the settings to view the price movement over a longer or shorter time frame in order to identify sell signals and resistance levels.
What is Sentiment
Analysis?
Since there are so many factors impacting the market and given the uncertainties surrounding every factor, it is impossible for traders and investors to accurately respond to each. Moreover, it is natural for traders to feel apprehensive when there is high volatility, or a series of unfavourable news. Similarly, traders feel more excited when there is a rally, or the news is overly favourable for certain financial instruments.
Given these, the financial market is not driven by fundamentals alone. There is another element at play, known as the market sentiment. This moves the market as much as any economic indicator, event, or news.
For instance, during the initial months of the covid-19 pandemic, the US dollar appreciated versus its major rivals. This was despite the fact that the US economy was threatened by skyrocketing daily infections and growing unemployment. The demand for the US dollar was driven by market sentiment.
On the one hand, tech stocks were rallying due to the growing dependence of people on tech solutions amid the shelter-in-place orders and ecommerce growth. Two individual stocks, both listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) that benefited were Shopify and Fastly. They have emerged through the pandemic looking stronger than ever. It was an unpredictable time for stock trading with fluctuations occurring across the board. This lifted demand for the currency.
On the other hand, investors and traders gravitated towards safe-haven options like the greenback due to concerns over the impact of the pandemic on the global economy. Despite fundamentals being hit and, on a downtrend, the US currency remained elevated, due to the overall mood of traders and investors. Similarly, there can be situations in which an overall negative mood can cause the price of a financial instrument to tumble, even with the fundamentals remaining the same or even improving. Negative sentiment will have more traders committing to a down position.
While all three approaches – fundamental, technical, and sentiment analysis - are important, it is a good idea to have a clear understanding of your financial goals and level of risk tolerance. Risk management is essential to any strategy and it will impact your trading style and trading decisions.
How to
Start Trading?
The global financial market offers numerous trading opportunities. To take advantage of these, the most important step is to choose the right online broker.

Regulation: You will be conducting online trading activities through the broker. This underlines the importance of choosing a regulated broker. There are different regulatory agencies that protect the best interest of traders in different countries. Some examples of such regulatory authorities are the ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission), the FCA (the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority) and the CySEC (Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission) which is often passported via the MiFID protocol across all European countries. A broker regulated by a leading regulatory authority will comply with the highest operating standards, including maintaining segregated accounts to protect the clients’ funds.

Financial instruments: Check out all the securities that the broker offers. Some offer a wide range of financial instruments, including more than 60 currency pairs, over 10,000 stocks, the most popular global indices (like US30, EURO50 and AUS200), commodities (like oil, coffee and cocoa), metals (like gold and silver) and cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin, Ripple and Ethereum). The product range of online Forex and CFD brokers continues to expand with many now offering exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Having such an elaborate offering has increased the demand for research and education.

Support: Some brokers offer tools like an economic calendar and forex calculator. They also provide live support so that traders have assistance whenever they need it the most.

Payment methods: Find out about the deposit and withdrawals methods offered by the broker. To make it super convenient for traders to deposit and withdraw funds, some offer several payment options, like credit and debit cards, domestic and international bank wires, Skrill, PayPal, Neteller, and more.

Cost of trading: Check the broker’s site for details of commissions and spreads. They may vary depending on the type of brokerage account that you have. Some brokers mention zero commission and then make money with wide spreads. On the other hand, you can trade with brokers that offer tight spreads, even as low as 0.0 pips. Consider contacting the broker to enquire about other costs.

Trading platform: MetaTrader 4 is by far the most popular platform used by forex traders. MT4 offers a number of helpful features, like easy-to-understand navigation, customisable interface, one-click trading of different financial instruments, real-time price streaming even on the demo account, secure trading with 128-bit encryption, Expert Advisors (EAs) for automated trading and customisable alerts. The MT4 platform is compatible with iOS, Android, Windows, and Mac, offering you the flexibility of trading at your convenience, even while you’re on the go. Choose a broker that offers popular trading platforms.

Research and education: A beginner needs to spend time learning the dynamics of the market and various aspects of trading. Some brokers understand this need and have invested in creating comprehensive trading education resources for beginners. This online library of resources could include ebooks, video tutorials, FAQs, glossary, newsletters, guides, and articles.

Trading accounts: Check out the value trading accounts details of minimum opening balance, spread, instruments, maximum leverage. minimum trade size, commission and more. Some traders also offer Islamic trading accounts.
The Bottom Line
Trading is a vast domain, with many factors impacting the markets. It is important to have a basic understanding of fundamental, technical and sentiment analysis. This helps you make more informed decisions. It is equally important to select the right broker, since this will determine how fast your orders are executed, how much support you will get while trading and the quality of tools you will use for analysis and trading.
Before you begin trading on a live account, it’s a great idea to open a demo account and practise trading in live market conditions with virtual money. This will help you get comfortable with the trading platform and become familiar with the market dynamics without risking your own funds. Demo accounts are also a great way to test trading strategies. Once you have a better understanding of market analysis and trading in general, you can open a live account and start trading for real.
 Access 10,000+ financial instruments
Access 10,000+ financial instruments Auto open & close positions
Auto open & close positions News & economic calendar
News & economic calendar Technical indicators & charts
Technical indicators & charts Many more tools included
Many more tools included
By supplying your email you agree to FP Markets privacy policy and receive future marketing materials from FP Markets. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Source - database | Page ID - 962