Read time: 7 Minutes
A trading strategy used for short-term or medium-term periods of time (time frame) and aims to generate profits from price fluctuations is generally classified as swing trading, derived from the price swing from one value to another. How traders and investors engage with the stock markets is unique to an individual’s circumstances. Some have full-time obligations; others are retired with time on their hands.
Swing trading entails entering trades with durations ranging from a few trading days to several months, with the intention of profiting from an anticipated change in stock prices or any financial instrument.
How does swing trading compare to other trading styles, including Scalping, Day Trading, and Position Trading?
- Scalping:
Scalping entails numerous daily trades in which positions are maintained briefly, often for only a few seconds; as a result, gains are minimal, but the risk can be decreased.
Scalping is considered an active trading style.
- Day Trading:
Day trading is typically carried out in a single day and is often a full-time job, with trades liquidated before the close of trade each day (5 pm EST). This can also allow day traders to devote more time to perfecting their trading approach.
Like scalping, day trading is an active style of trading.
- Position Trading:
A position trader is a trader who purchases an asset as more of an investment for the long term to profit from an increase in the asset’s value.

Swing Trading Strategies
Below are four swing trade strategies commonly used to identify trading opportunities. This enables market participants to manage trades from start to finish. As with any investment, though, it’s advised to have a fully tested trading plan in place.
- Fibonacci Retracements
On the charts, the Fibonacci retracement tool can be utilised to assist traders in locating levels of support and resistance; consequently, there are levels that may signal a possible trend reversal. Plotting horizontal lines at the classic Fibonacci ratios of 38.2% and 61.8% on a chart can reveal potential reversal levels within trending environments. Because currencies, as well as stocks and other financial assets, frequently retrace a certain percentage within a trend before reversing again, Fibonacci levels can offer dip-buying scenarios and sell-on rally setups. Even though it does not fit the Fibonacci pattern, traders also look at the 50% level because markets tend to reverse direction after retracing half of the previous move.
- Support and Resistance
Support and resistance lines are the bedrock of technical analysis, and you’ll find traders and investors frequently build swing trading strategies on their foundation.
A support level is a price level or area on a price chart below the current market price action at which buying pressure has been sufficient to overcome selling pressure. As a result, a price decline is generally halted, and prices rise again. A swing trader can, therefore, place a protective stop-loss order below the support line and enter a buy trade on the basis of a bounce off the support line.
Opposite of support is resistance. It is a price level or region above the current market price where selling pressure has overcome buying pressure in the past. In this scenario, a swing trader could enter a sell position on the rebound from the resistance level and place a protective stop-loss order above the resistance line. When incorporating support and resistance into your swing trading system, it is important to keep in mind that when a price move breaches a support or resistance level, their roles often switch. What was once a support becomes a resistance and vice versa.
- Moving Averages (MAs)
Utilising MAs is another prevalent swing trading strategy. SMAs, or simple moving averages, smooth out price data by calculating an average price that is constantly updated and can be taken over a variety of specific time periods or lengths. For example, a 10-day SMA calculates a new daily average by adding the daily closing prices for the previous 10 days and dividing by 10 (the number of observations). The employed length (10) can be applied to any chart interval, from one minute to one week. Shorter SMAs respond more quickly to price changes than their longer counterparts.
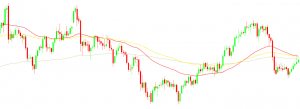
With the 10- and 20-day SMA swing trading system, for example, two SMAs of these durations are applied to a stock chart. A buy signal is generated when the shorter SMA (10) crosses above the longer SMA (20), indicating a possible uptrend. Conversely, a sell signal is generated when the shorter SMA crosses below the longer-term SMA as this crossover indicates a downward trend.
- MACD Crossover
The MACD crossover swing trading system provides a straightforward method for identifying swing trading opportunities. It is one of the most widely used indicators to determine trend direction and reversals. The MACD consists of two moving averages, the MACD line (difference between the 26-day EMA and 12-day EMA) and the signal line (9-day EMA of the MACD), which generate buy and sell signals when they cross. If the MACD line crosses above the signal line, a bullish trend is signalled, and a buy trade could be considered. A bearish trend is likely if the MACD line crosses below the signal line and a sell recommendation is made. Before exiting the trade, a stock swing trader would wait for the two lines to cross again, signalling a trade in the opposite direction.
The MACD oscillates around a centreline, and buy and sell signals are generated when the MACD crosses above or below the centreline. What this means is the 12-day EMA has crossed above the 26-day EMA if the MACD is above the centreline, and vice versa for a MACD bearish centreline cross.
Conclusion
Swing traders use their investment strategies and analysis styles to find a market’s most effective entry and exit points. That analysis might include fundamental analysis (data from economic reports) or technical analysis (chart patterns and technical indicators, for example), or a combination of both, to optimise trading opportunities.
Head over to the FP Markets education section to gain valuable insights for beginners and experts alike, where you can also open a demo or live trading account to test any swing trading strategies.







 Access +10,000 financial
instruments
Access +10,000 financial
instruments

